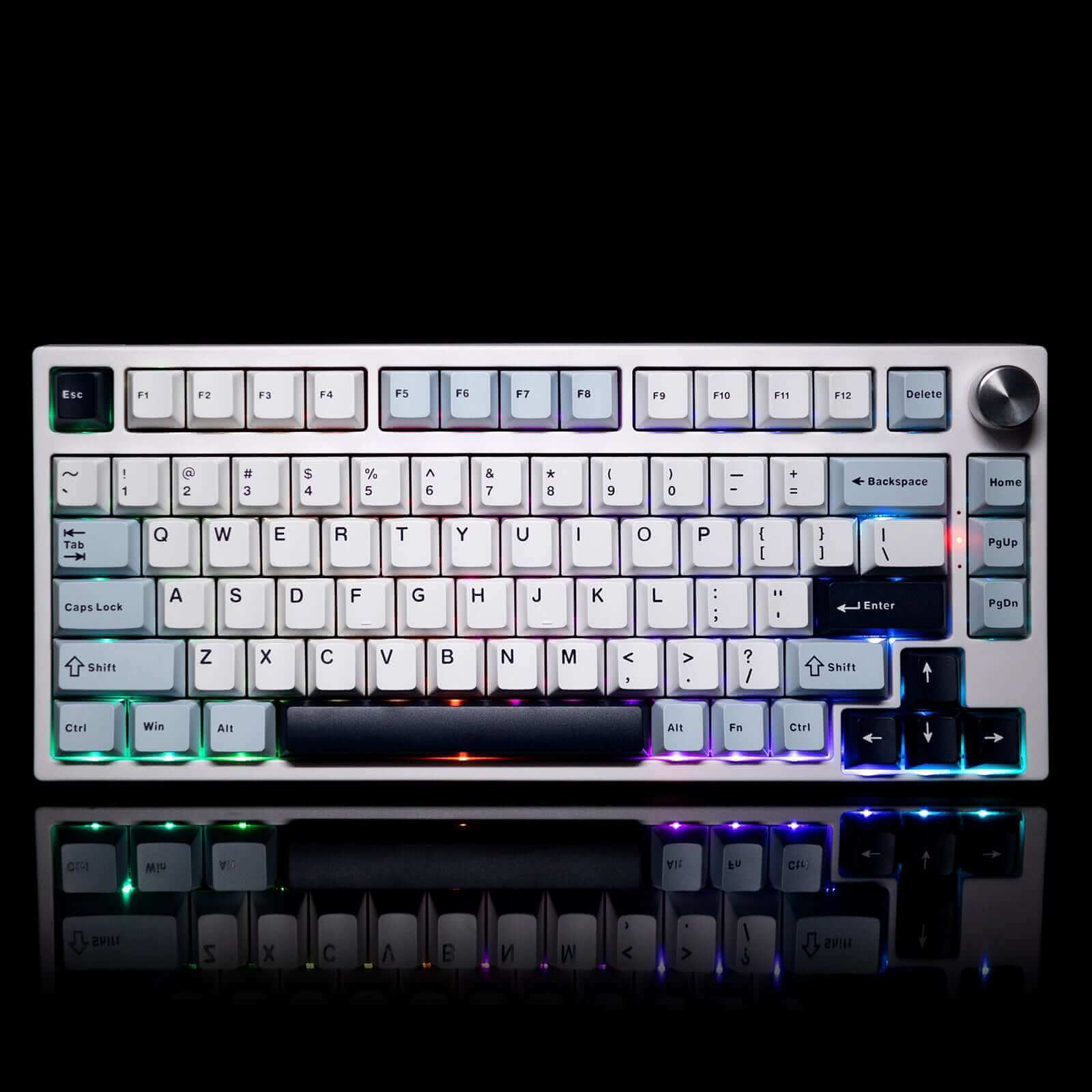
Hall effect keyboards are making a comeback. Actually, it is not a new technology. If you Google it you may find that the Hall effect keyboard and switch can be traced back to 60 years ago. You can also see this technology used in common places, for example: iPad protective cases.
So what is the Hall effect and how does it work? Let’s check it out:
Gamakay TK75HE V2 Hall Effect Keyboard
How does the Hall Effect work?
The Hall effect occurs when a conductor or semiconductor carrying current is placed in a magnetic field. The magnetic field deflects free electrons to one side, creating a voltage difference across the material. This voltage is perpendicular to both the current and the magnetic field. The Hall effect is used in Hall sensors, in measuring magnetic field strength, and in electronic devices such as keyboards with magnetic switches.

From: telcontar
In a keyboard, by setting a voltage threshold for each key, the key is registered as pressed when the Hall voltage exceeds that threshold. This is the logic of the magnetic switch implementation.
What is a Magnetic Switch?
The construction of a magnetic switch is simple: a shaft center, a magnet, a Hall sensor, and a spring. When pressed, the magnet approaches the Hall sensor, generating a Hall voltage above the threshold, which in turn triggers the input.

From: telcontar
What are the advantages of the Hall Effect?
1. Dynamic Keystroke (DKS): Allows up to four different actions within a single keystroke, providing macro-like customization for gaming and productivity.
2. Travel Distance Setting: Adjustable actuation from 0.2 mm to 3.7 mm, letting users fine-tune typing feel.
3. Rapid Trigger: Keys activate/deactivate based on travel distance instead of a fixed point, enabling faster and more precise inputs.
Future of Hall Effect Keyboards
Compared to traditional mechanical keyboards, Hall Effect keyboards will evolve in both hardware and software, offering more advanced customization. Some Hall Effect PCBs may support hot-swap, but factory calibration ensures precision. With AI calibration and software, the typing experience can be fully customized.

Gamakay’s Silent-Phoenix and Linear Mercury switches
The upcoming Gamakay TK75HE V2 will be equipped with Silent-Phoenix and Linear Mercury magnetic switches, both built with Hall sensors.
The Silent-Phoenix builds on mechanical Silent-Phoenix, reducing typing noise, perfect for office workers or late-night gamers.
The Linear Mercury Switches
The Gamakay Mercury is a smooth and quiet linear switch. In the magnetic version, it delivers faster response and a seamless typing experience, ideal for competitive gaming.
Gamakay firmware supports features such as:
- Custom DKS trigger points
- Calibration of trigger accuracy
- Four factory preset modes (Gaming, Fast Typing, Comfort, Custom)

Comfort mode balances trigger sensitivity for everyday typing.
Overall, Hall Effect technology brings unique advantages to keyboards, and its future development promises more customization and better user experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hall Effect Keyboards
Q: What is a Hall Effect keyboard?
A: A keyboard using magnetic switches with Hall sensors to detect keypresses, eliminating contact wear and providing higher durability and precision.
Q: What are the advantages of Hall Effect switches?
A: They enable Rapid Trigger, Dynamic Keystroke (DKS), adjustable actuation points, and smoother, quieter operation compared to traditional switches.
Q: Does Gamakay offer a Hall Effect keyboard?
A: Yes. The latest Gamakay TK75HE V2 Hall Effect keyboard comes with magnetic switches, 0.005 mm precision, Snap Tap, and customizable trigger points.
Q: Can Hall Effect switches be hot-swapped?
A: Some PCBs support it, but most are factory calibrated. The TK75HE V2 supports software calibration for precise accuracy and supports hot-swappable
Q: Why does my W key sometimes stop working on a Hall Effect keyboard?
A: This can happen if the actuation point is set too shallow or deep. You can recalibrate or reset the key in the keyboard software to fix it.